This article provides a clear overview of IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) and Surrogacy, two major fertility treatments used to help individuals or couples achieve parenthood. You’ll learn what each method involves, how they differ in process and purpose, and the key medical, emotional, and legal aspects to consider before choosing the most suitable option.
Quick Answer – Main Difference Between IVF and Surrogacy
IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) is a fertility treatment in which an embryo is created outside the body and then implanted into the intended mother’s uterus, allowing her to carry the pregnancy herself. Surrogacy, on the other hand, involves another woman—a surrogate mother—carrying the pregnancy for the intended parents, either because the intended mother cannot carry a pregnancy or chooses not to. In short, IVF allows the mother to be pregnant herself, while surrogacy relies on a surrogate to carry the baby.
What Is IVF?
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is the most common form of assisted reproductive technology (ART) used to help individuals or couples with difficulty conceiving naturally. According to Choe and Shanks (StatPearls, 2023), IVF involves retrieving eggs from the intended mother or a donor, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory, and transferring the resulting embryo into the uterus to achieve pregnancy. The first successful IVF birth was reported in 1978 by Robert Edwards and Patrick Steptoe in England, marking a major breakthrough in infertility treatment (Choe & Shanks, 2023). Today, IVF is widely applied for infertility caused by tubal disease, endometriosis, male factor infertility, or age-related decline in egg quality, and it has helped millions of people worldwide to achieve pregnancy (Choe & Shanks, 2023).
What Is Surrogacy?
Surrogacy is a form of assisted reproductive technology (ART) in which a woman, known as the surrogate mother, carries and delivers a child for another individual or couple, referred to as the intended or commissioning parents. The term “surrogate” comes from the Latin “subrogare”, meaning “to substitute” — literally, “to act in place of another.”
According to Dr. Nayana Hitesh Patel and colleagues in their review published in the Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences (2018), surrogacy enables individuals or couples who are unable to carry a pregnancy due to medical, anatomical, or social reasons to experience parenthood. This includes women without a uterus, those with severe uterine abnormalities, or individuals for whom pregnancy poses serious health risks. It also provides opportunities for same-sex male couples and single men to become biological parents through IVF using donor oocytes.
There are two main types of surrogacy: traditional and gestational.
In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate is inseminated with the intended father’s sperm and is genetically related to the child.
In gestational surrogacy, the embryo is created via IVF using the gametes of the intended parents or donors and transferred into the surrogate’s uterus — meaning she has no genetic link to the baby.
Dr. Patel’s study also highlights two distinct arrangements — commercial and altruistic surrogacy. In commercial surrogacy, the surrogate receives monetary compensation beyond medical expenses, whereas in altruistic surrogacy, she is reimbursed only for pregnancy-related costs and provided insurance coverage.
As Dr. Patel concludes, surrogacy “has proved to be a blessing and medical marvel for many couples,” allowing those who cannot conceive or carry a child to achieve biological parenthood when practiced ethically and safely under medical supervision.

Key Differences Between IVF and Surrogacy
While both IVF and surrogacy are assisted reproductive technologies designed to help individuals or couples achieve parenthood, their processes and purposes differ significantly.
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM, 2022) and Mayo Clinic, the key difference lies in who carries the pregnancy.
In IVF (In Vitro Fertilization), the woman undergoing treatment is both genetically and physically the mother who carries the embryo. In surrogacy, however, the embryo—created via IVF—is transferred into another woman’s uterus (the surrogate), who carries the pregnancy on behalf of the intended parents.
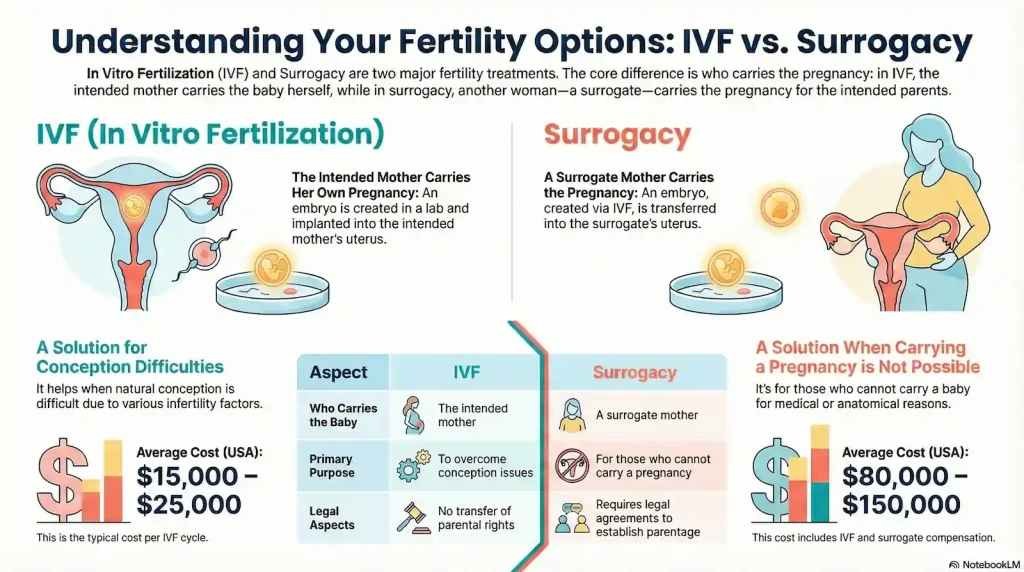
The following table summarizes the main distinctions between IVF and surrogacy:
| Aspect | IVF | Surrogacy |
|---|---|---|
| Who carries the baby | The intended mother | A surrogate mother |
| Genetic link | The baby is genetically related to both intended parents (unless donor eggs/sperm are used) | The baby is genetically related to the intended parents, not the surrogate (in gestational surrogacy) |
| Purpose | Helps individuals conceive when natural conception is difficult | Helps individuals who cannot carry a pregnancy due to medical or anatomical reasons |
| Medical process | Egg retrieval, fertilization, and embryo transfer into the intended mother | IVF performed first, then embryo transfer into a surrogate’s uterus |
| Legal aspects | No legal transfer of parental rights | Legal agreements required to establish intended parents’ rights |
| Emotional considerations | Direct physical and emotional involvement in pregnancy | Emotional complexity due to involvement of a third party |
| Average cost (USA) | $15,000 – $25,000 per IVF cycle | $80,000 – $150,000 including IVF and surrogate compensation |
Final Summary
In summary, the main difference between IVF and surrogacy lies in who carries the pregnancy.
In IVF (In Vitro Fertilization), the intended mother’s eggs are fertilized in a laboratory and the resulting embryo is placed in her own uterus to achieve pregnancy.
In surrogacy, the embryo is created through IVF and transferred into another woman’s uterus—the surrogate—who carries the baby on behalf of the intended parents.
While IVF is ideal for couples struggling with infertility but able to carry a pregnancy, surrogacy is the best option when carrying a child is medically impossible or unsafe. Both methods offer the chance to build a biological family through modern reproductive technology.
If you’re considering IVF or surrogacy, our fertility specialists at VitaLife can guide you toward the most suitable and affordable solution based on your personal and medical circumstances.
At VitaLife, we provide a comprehensive Surrogacy in Iran program specifically designed for international intended parents. We offer a transparent, all-inclusive service that combines advanced medical care with full legal support, making the dream of parenthood both accessible and secure.